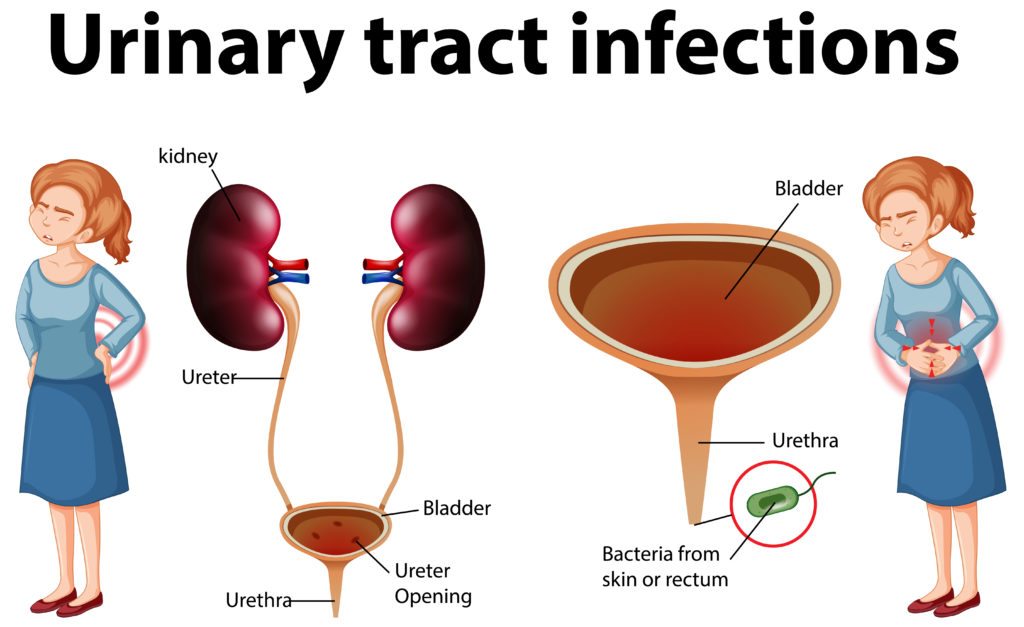
Inspirating Tips About How To Detect Kidney Disease
Call 911 or go to your nearest emergency room if you develop the following signs and symptoms of acute kidney injury:
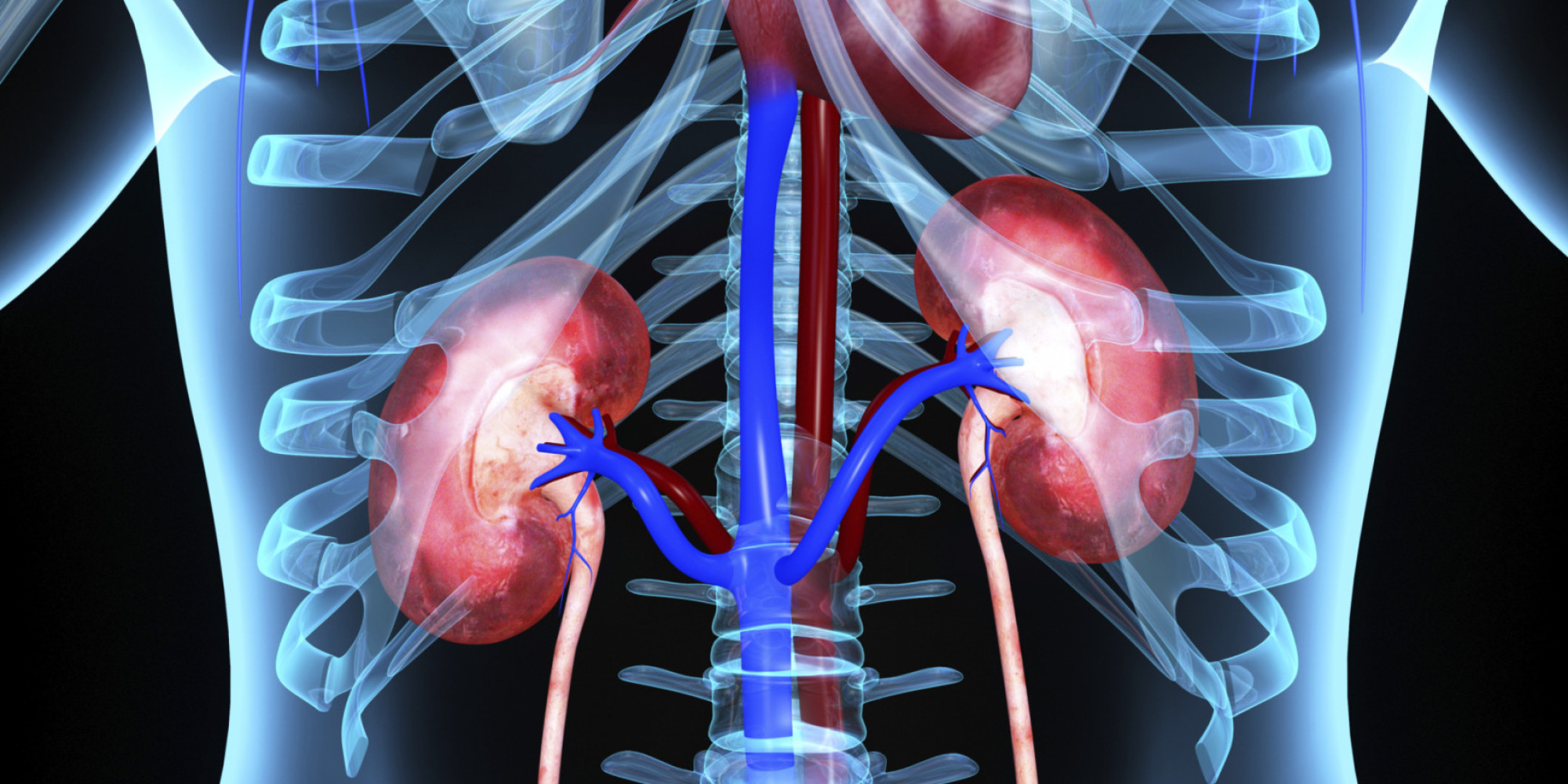
How to detect kidney disease. Chronic kidney disease (ckd) is best identified and treated early as part of comprehensive primary medical care. A simple measurement. Both tests are needed to have a clear picture of your kidney health.
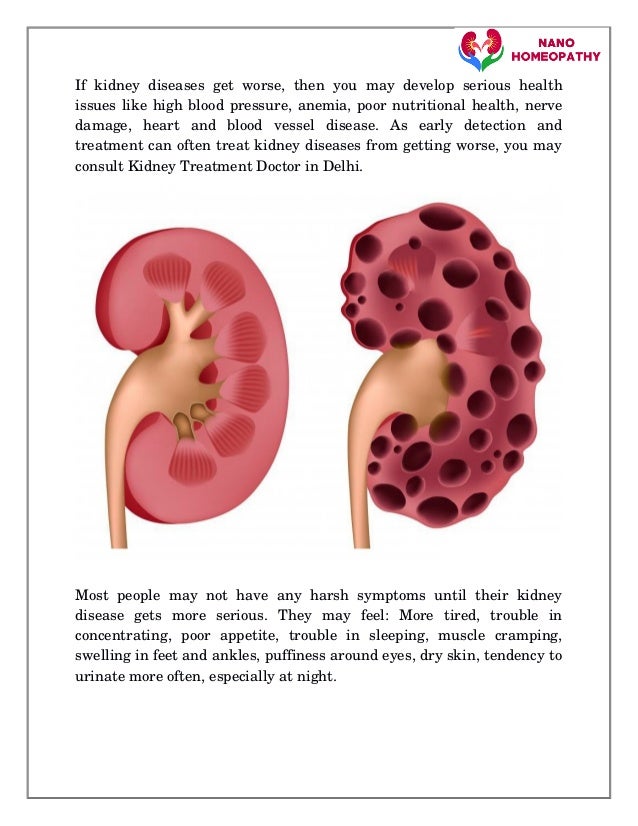
High potassium ( hyperkalemia ), which affects your heart’s ability to function correctly. Kidney disease affects an estimated 37 million people in the united states, which is about 15% of the adult population, according to the foundation. Albumin is a protein that can pass into the urine when the kidneys are damaged.
In this editorial from the special issue “chronic kidney. A blood test that checks how well your kidneys are filtering your blood, called gfr. If you’re at risk for kidney disease due to high blood pressure, diabetes, a family history of kidney failure or if you’re older than age 60, it’s important to get tested annually for kidney disease.
The risk of developing dangerous symptoms increases with age, with those who are age 85 and older are at the highest risk of serious symptoms. The test may be repeated once or twice to confirm the results. Early detection can help prevent the progression of kidney disease.
Here are five ways we are leading the charge towards a fairer future. You should see a healthcare provider if you have any signs of kidney disease but may need to do so urgently if the symptoms develop suddenly and severely. Gfr assesses how efficiently your kidneys clear waste from your system.
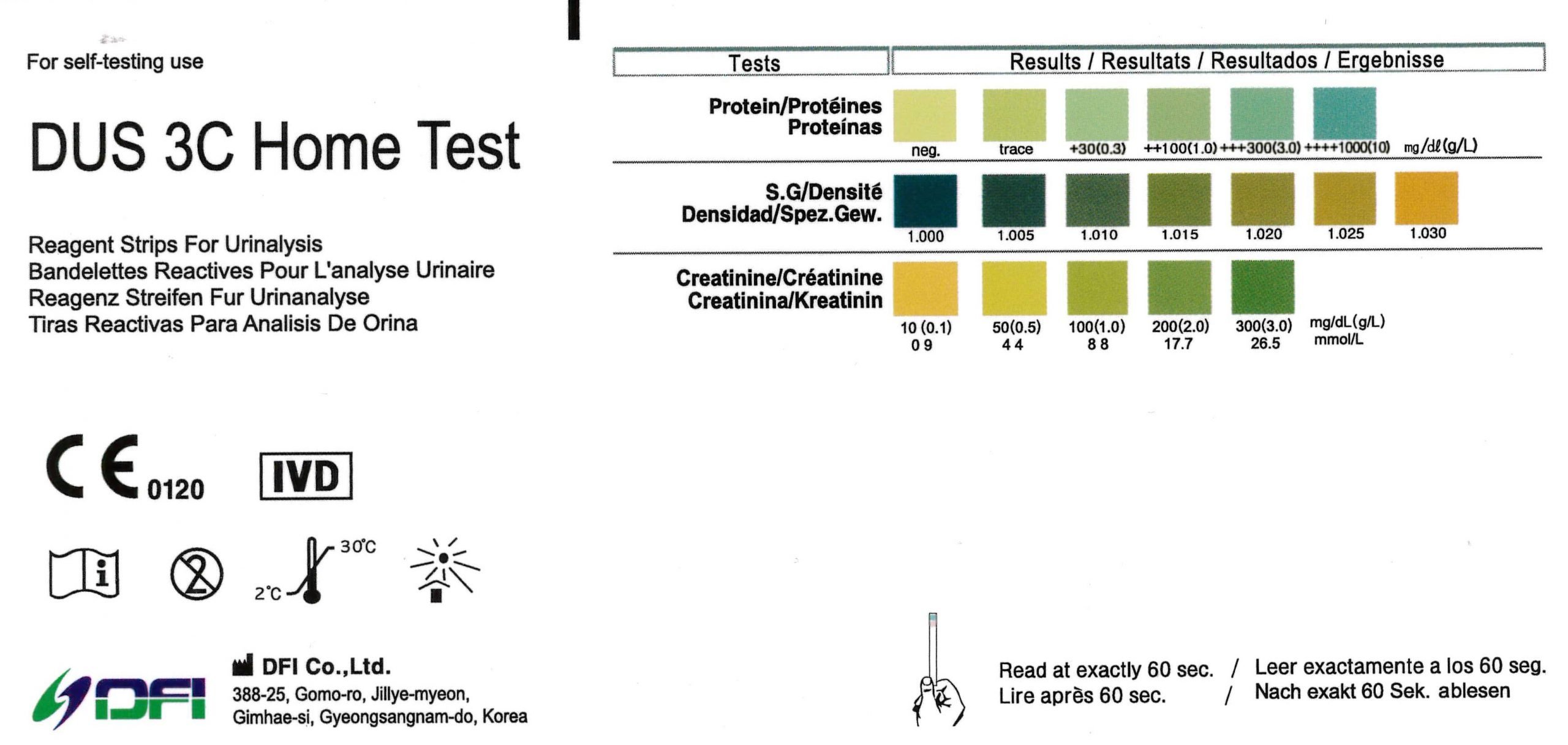
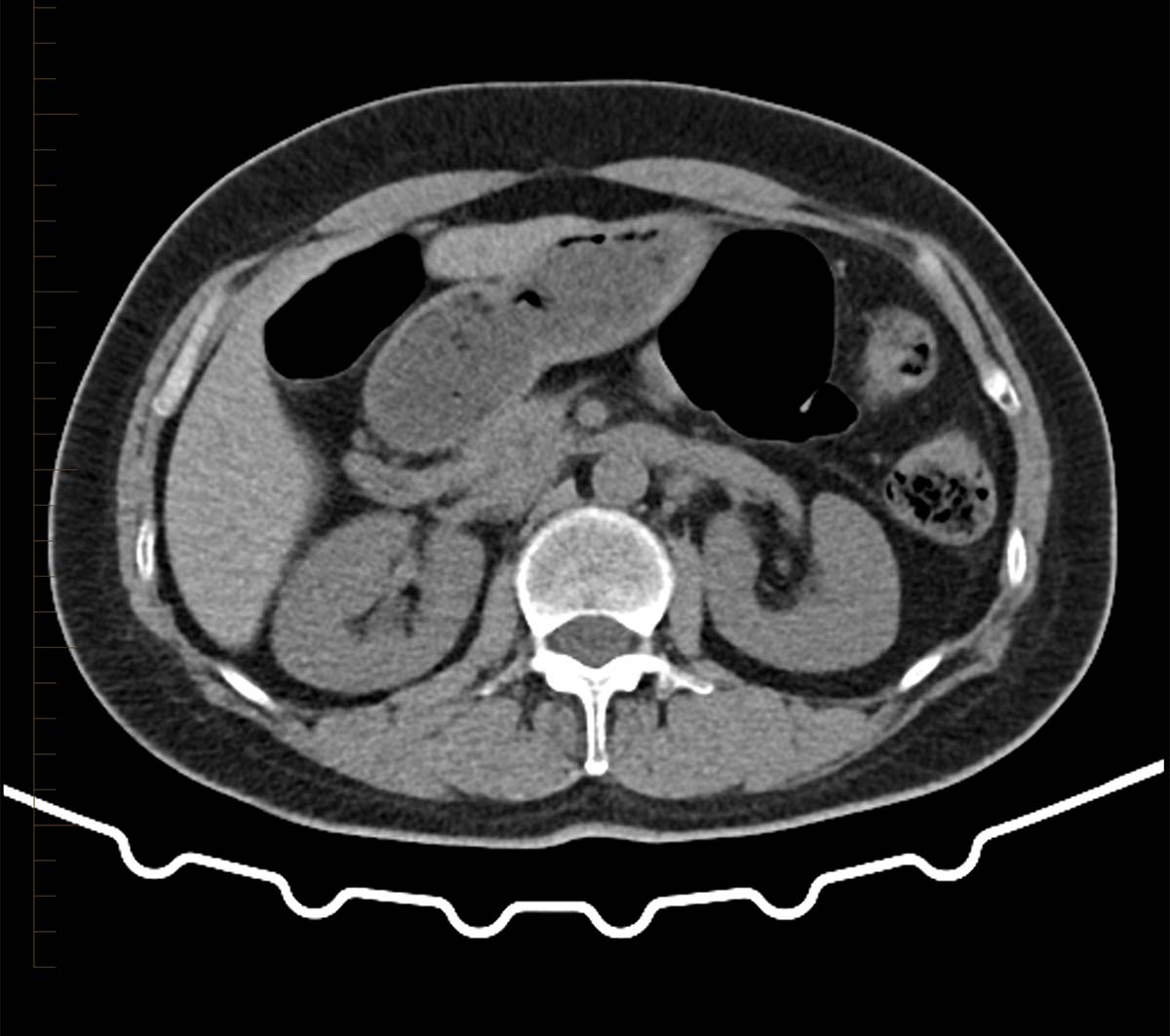
Other imaging tests might be used in some cases. Renal failure tests can include blood and urine tests to measure how well your kidneys are filtering out waste and to check for proteins like albumin. A urine test can help doctors find any abnormalities in the urine.
Although chronic kidney disease (ckd) can be detected by relatively simple blood and urine tests, it remains underdiagnosed even in patients at high risk for the disease. Detecting chronic kidney disease by electrocardiography. Chronic kidney disease (ckd) is primarily diagnosed with blood and urine tests that detect chemical imbalances caused by the progressive loss of kidney function.
Kidney function tests are urine or blood tests that evaluate how well your kidneys are working. Currently, the key markers used include abnormal urine albumin levels and a persistent reduction in the estimated glomerular filtration rate (egfr). Diagnosing kidney disease • a kidney biopsy is evaluated using the latest technology, electron microscopy • for people whose doctors suspect kidney disease based on symptoms such as blood in the urine • the next step may be treatment with medication or in severe cases dialysis or transplantation • involves pathology and nephrology related.
Weight loss or poor appetite swollen ankles, feet or hands (oedema) shortness of breath tiredness blood in your pee (urine) peeing more than usual, particularly at night the gp can look for other possible causes and arrange tests if necessary. It’s important to know that: To diagnose renal failure, a doctor may order several tests.
Heart disease and blood vessel disease, including increased risk of stroke and heart attack. Be sure to mention any symptoms you’re experiencing to your healthcare practitioner. The early stages of chronic kidney disease may not have symptoms, but kidney failure symptoms may include feeling sick, confusion, swelling and peeing a lot.












:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/kidney-disease-diagnosis-5b2d5a33ff1b780037ad002f.png)